AI All-Over

Key Takeaway:
While AI adoption globally today is more than double that in 2017, according to McKinsey, the proportion of organizations using AI has leveled off to around 50-60% in recent years. However, Generative AI (GenAI) marks a tipping point for AI with its ability to generate new content (such as text, audio, video, images, code, or even protein sequences) from similar formats of unstructured data. It can automate many tasks, boost productivity, reduce costs, and provide multiple growth opportunities. Those are key reasons why, according to the World Economic Forum, by 2026, mWhile AI adoption globally today is more than double that in 2017, according to McKinsey, the proportion of organizations using AI has leveled off to around 50-60% in recent years. However, Generative AI (GenAI) marks a tipping point for AI with its ability to generate new content (such as text, audio, video, images, code, or even protein sequences) from similar formats of unstructured data. It can automate man
Trend Type: Technology
Sub-trends: Democratized GenAI, GenAI Adoption, Corporate AI Agenda, Applied AI, GenAI expansion into the business world, AI Business Model, Artificial General Intelligence, AI Reality Check, Multimodal AI;
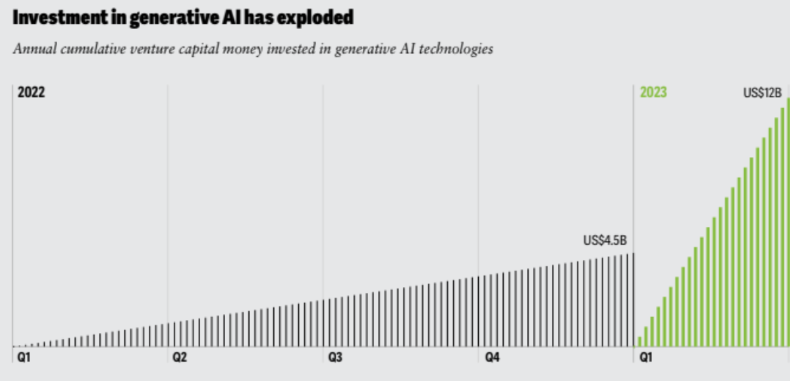
GenAI’s Enterprise Adoption
Use Cases
GenAi Adoption: OTP Bank generated a Hungarian large-language model to enable more than 30 banking use cases across the organization, with an initial focus on spoken and txt customer interactions, fraud detection, and cybersecurity.
Applied AI: Emirates Team New Zealand accelerated hydrofoil design and testing by using AI to train a “digital twin” – a digital replica of a sailor – to test designs in a simulated environment.
Use Cases
Sub-Trend Sources
Democratized GenAi: Gartner Strategic Trends, Kyndryl, Kantar's Media Trends, Deloitte Tech Trends, WEF Jobs of Tomorrow GenAI, McKinsey Tech Trends Outlook, McKinsey Economic Potential of GenAI, Finance & Development
GenAI Adoption: BBVA Spark Tech Trends, Forbes Tech Predictions, McKinsey Tech Trends Outlook, Bruegel.org - Exposure of GenAI to European Labour Market
Corporate AI Agenda: HBR Tech Trends
Applied Ai: McKinsey Tech Trends Outlook, McKinsey Beyond the Hype
GenAI expansion into the business world: Cisco Trends
AI Business Model: HBR Tech Trends
Artificial General Intelligence: Benedict Evans, Future Today Institute, Finance & Development
AI Reality Check: IBM AI Trends, Future Today Institute, PWC AI Trends, McKinsey GenAi Reset
Multimodal AI: CBInsights Emerging Tech Trends
Small AI: HBR Tech Trends
GenAi: Small is the new big | Capgemini
What to Read Next
All Things Data
The increasing complexity and scale of data within modern enterprises lead into a shift in data management strategies, catalyzing a trend towards more dynamic, integrated, and technologically advanced approaches. This[...]
Quantum Computing
Latest Advances Although Quantum Computing was already present in last year’s Digital Trends, in 2024, the race to develop viable quantum systems is intensifying, with tech giants like IBM, Google,[...]
Eco Tech
The “Eco Tech” trend reflects the growing integration of technology with environmental sustainability efforts. Among the forefront technologies is carbon capture. Industries such as cement and steel are increasingly adopting[...]
What to Read Next
All Things Data
The increasing complexity and scale of data within modern enterprises lead into a shift in data management strategies, catalyzing a trend towards more dynamic, integrated,[...]
Quantum Computing
Latest Advances Although Quantum Computing was already present in last year’s Digital Trends, in 2024, the race to develop viable quantum systems is intensifying, with[...]
Eco Tech
The “Eco Tech” trend reflects the growing integration of technology with environmental sustainability efforts. Among the forefront technologies is carbon capture. Industries such as cement[...]


