Augmented Software

Key Takeaway:
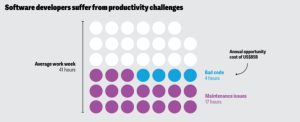
The integration of artificial intelligence into software development tools, known as "Augmented Software," is transforming the technological strategies of companies. This trend is driven by the need to enhance efficiency, cut costs, and capitalize on the potential of open-source solutions. Tools like GitHub’s Copilot and Amazon's CodeWhisperer are pioneering this shift by enabling more accurate and holistic code generation from natural language, significantly boosting developer productivity and satisfaction. Despite these advances, adoption faces hurdles such as technical challenges and the need for retraining. However, promising early productivity gains suggest wider adoption soon. Financially, the impact is notable, with predictions of up to a $10 billion revenue increase by 2024 for enterprise software companies, indicating a robust market potential that could extend far beyond 2025.
Trend Type: Technology
Sub-trends: Enterprise-Grade Open-Source Software, DIY Software, GenAI & Enterprise software, AI Augmented development, Platform Engineering, SQL optimization becomes a priority.
However, Generative AI (GenAI) marks a tipping point for AI with its ability to generate new content (such as text, audio, video, images, code, or even protein sequences) from similar formats of unstructured data.
Use Cases
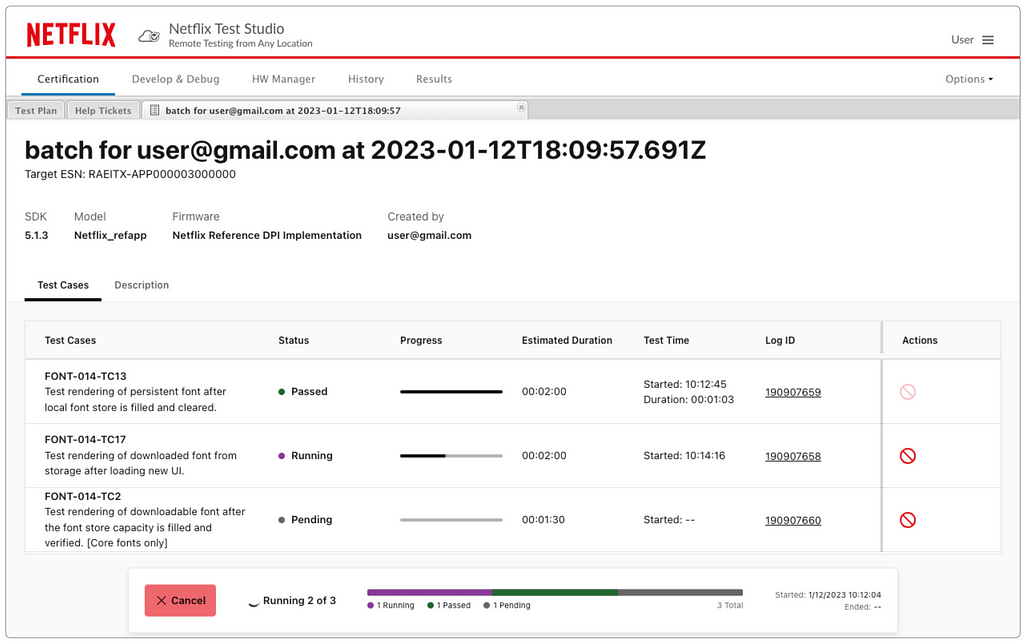
DIY Software: Netflix built Netflix Test Studio (NTS), which supports a seamless streaming experience on many types of devices. NTS is a cloud-based automation framework for developers to deploy and execute tests. NTS runs more than 40K long-running tests every day and allows remote tests of Netflix-ready devices.
AI Augmented development: Vistra partnered with McKinsey to develop more than 400 AI models and used MLOps to standardize their deployment and maintenance. This enabled the company to optimize the thermal efficiency across 26 of its plants, generate more than $20 million in energy savings, and abate about 1.6 million tons of carbon per year.
Sub-Trend Sources
Enterprise-Grade Open-Source Software: BCG The Next Wave
DIY Software: CBInsights Emerging Tech Trends, Thoughtworks Tech Radar, McKinsey Tech Trends Outlook, Deloitte Tech Trends
GenAI & Enterprise software: Delloite TMT Predictions, Forrester Predictions, McKinsey Economic Potential of GenAI
AI Augmented development: Gartner Strategic Trends, McKinsey Tech Trends Outlook
Platform Engineering: Gartner Strategic Trends
SQL optimization becomes a priority: BMC Blogs IT TrendsBMC Blogs IT Trends
What to Read Next
All Things Data
The increasing complexity and scale of data within modern enterprises lead into a shift in data management strategies, catalyzing a trend towards more dynamic, integrated, and technologically advanced approaches. This[...]
Quantum Computing
Latest Advances Although Quantum Computing was already present in last year’s Digital Trends, in 2024, the race to develop viable quantum systems is intensifying, with tech giants like IBM, Google,[...]
Eco Tech
The “Eco Tech” trend reflects the growing integration of technology with environmental sustainability efforts. Among the forefront technologies is carbon capture. Industries such as cement and steel are increasingly adopting[...]
What to Read Next
All Things Data
The increasing complexity and scale of data within modern enterprises lead into a shift in data management strategies, catalyzing a trend towards more dynamic, integrated,[...]
Quantum Computing
Latest Advances Although Quantum Computing was already present in last year’s Digital Trends, in 2024, the race to develop viable quantum systems is intensifying, with[...]
Eco Tech
The “Eco Tech” trend reflects the growing integration of technology with environmental sustainability efforts. Among the forefront technologies is carbon capture. Industries such as cement[...]