Scientific AI

Key Takeaway:
AI is accelerating scientific progress across disciplines—from protein folding to materials discovery and precision health. As open-source platforms like LeMaterial emerge and Nobel-recognized breakthroughs like AlphaFold inspire new applications, companies are increasingly turning to AI not just for data analysis but for hypothesis generation and experimentation. In healthcare, AI-enabled symptom checkers, early disease detection, and predictive analytics are reshaping diagnosis and treatment. With growing investment and adoption from players like Meta, Google, and Mayo Clinic, "Scientific AI" is rapidly evolving from lab tool to core engine of discovery.
Trend Type: Technology
Sub-trends: Scientific AI, Precision Health, RNA Therapeutics, Healthspan
AI Meets Scientific Discovery
A new frontier is opening where AI is not merely a support tool for scientific research—it’s becoming a catalyst for fundamental breakthroughs. This shift was symbolically recognized in October 2023, when the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to DeepMind’s Demis Hassabis and John Jumper for developing AlphaFold, a tool capable of predicting protein structures, and to David Baker, who built complementary tools for designing new proteins. The award was unprecedented: the first time a Nobel recognized an AI system as a scientific collaborator. It marked the coming of age of “Scientific AI”—a paradigm in which machine intelligence actively contributes to natural science discovery.
Proteins were an ideal use case: the field had well-structured data, making it ripe for training high-performance models. But AlphaFold was just the beginning. The race is now on to replicate this success in fields like materials science, chemistry, and biology. Meta has released expansive open-source datasets and models aimed at accelerating materials discovery. In December 2024, Hugging Face and Entalpic launched LeMaterial, an initiative to clean and unify fragmented materials science datasets to facilitate faster experimentation and innovation. These efforts reflect a shift in how knowledge is produced—one where model development, dataset standardization, and collaborative platforms drive scientific productivity.
Today, AI is reshaping several key stages of the scientific process. It is helping researchers formulate better research questions by identifying knowledge gaps in existing literature, refine hypotheses through data-driven pattern recognition, and accelerate data collection and analysis by automating experiments, simulations, and real-world observations. While human creativity remains essential, AI is becoming an active co-pilot across the early and middle phases of scientific inquiry, setting the stage for faster, more scalable discovery.
Precision Health and the Shift to Proactive Care
The impact of Scientific AI is particularly visible in healthcare, where AI systems are reshaping how diseases are predicted, detected and treated. According to CB Insights’ latest “Symptom Checkers & Provider Discovery” market report (November 2024), companies are rapidly developing AI tools that evaluate patient-reported symptoms through chatbot-style interfaces, then match them against disease databases to suggest diagnoses and appropriate care. GYANT, Ubie, Sensely, and Loyal are among the startups drawing investment or acquisition interest in 2024, with players like Google Ventures and Fabric leading the charge.
But this trend goes beyond digital triage. AI is increasingly enabling early disease detection—sometimes even before symptoms appear. A wave of high-momentum startups is pushing forward the “proactive healthcare” model, where interventions are guided by AI insights drawn from large population data. Among them are companies focused on oncology, neurology, cardiology, and rare diseases—many with commercial partnerships spanning Novartis, AstraZeneca, and Siemens Healthineers. As CB Insights notes, many of the leading startups in this space are scaling quickly—both in terms of geographic reach and integration into hospital systems.
One of the most promising players is Lucem Health, a Mayo Clinic and AWS-backed startup that helps providers mine existing datasets to identify high-risk patients without direct testing. Its approach leverages patient history, diagnostics, and environmental factors to flag early warning signs at scale. It’s not alone. These developments reflect a broader movement from reactive to preventative care. AI is no longer confined to back-office data crunching; it is moving to the clinical frontlines, helping providers deliver faster, more accurate, and more personalized interventions.
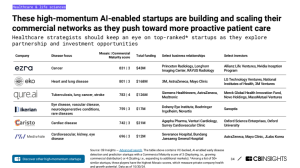
Source: CB Insights: AI-Enabled Startups in Different Medical Fields
Toward Autonomous Scientific Discovery
The vision behind Scientific AI is both ambitious and provocative: that AI systems could someday autonomously generate and test scientific hypotheses, run virtual experiments, and even design new molecules or materials. While such autonomy is still speculative, steps toward this future are accelerating.
Companies like DeepMind, Meta, and Anthropic are not merely releasing models—they’re rethinking what it means to automate scientific reasoning. For example, Meta’s Open Catalyst project trains AI to predict chemical reactions that could lead to better energy storage, a key enabler for green technologies (check the “Energy Challenge” trend for more). Meanwhile, Anthropic’s focus on interpretability and alignment lays the groundwork for AI systems that can explain their “thought processes”—a necessity in regulated scientific domains.
A major bottleneck remains data. Unlike consumer applications, scientific domains often suffer from fragmented, inconsistent, or non-digitized datasets. That’s why initiatives like LeMaterial are so critical. By curating, cleaning, and standardizing the raw material of research, they lower the barrier to AI-driven discovery and open the door to reproducible science at scale.
Still, challenges persist. Regulatory approval, explainability, and the black-box nature of some AI models pose hurdles to widespread adoption in scientific settings. Collaboration between tech companies, universities, hospitals, and governments will be key to translating AI potential into real-world breakthroughs.
Use Cases
Precision Health: What if AI could tell us we have cancer before we show a single symptom? Steve Quake, head of science at the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, explains how AI can revolutionize science.
Precision Medicine: Each of us is completely unique, and our health journey should be too. If AI can transform healthcare for the better, empowering health providers to deliver more personalized, tailored care on a global scale should be the way. See what could be possible in the not-too-distant future.
Use Cases
Sub-Trend Sources
Scientific AI: MIT 5 Trends in AI and Data Science
Precision Health: CB Insights Tech Trends, MIT 10 Breakthrough Technologies
RNA Therapeutics: CB Insights Tech Trends
Healthspan: Euromonitor Top Global Consumer Trends, Marian Salzman, Trend Hunter, VML The Future 100.
What to Read Next
Energy Challenge
The Collision of AI and Energy Demand The rise of generative AI is not only transforming digital landscapes—it’s also reshaping the global energy equation. According to Deloitte, the rapid expansion[...]
AI Agents
The Emergence of Agentic AI: From Tools to Autonomous Decision-Makers AI agents—software systems capable of independently completing complex tasks—are becoming one of the most closely watched innovations in the GenAI[...]
Embodied AI
Embodied AI and Robotics The integration of foundation models into robotics is revolutionizing how machines interact with the world, enabling them to reason, adapt, and operate autonomously in dynamic environments.[...]
What to Read Next
Energy Challenge
The Collision of AI and Energy Demand The rise of generative AI is not only transforming digital landscapes—it’s also reshaping the global energy equation. According[...]
AI Agents
The Emergence of Agentic AI: From Tools to Autonomous Decision-Makers AI agents—software systems capable of independently completing complex tasks—are becoming one of the most closely[...]
Embodied AI
Embodied AI and Robotics The integration of foundation models into robotics is revolutionizing how machines interact with the world, enabling them to reason, adapt, and[...]


